Genitourinary Trauma
Injuries to the lower genitourinary (GU) tract alone are not life threatening, but their association with other potentially more significant injuries necessitates an organized approach to diagnosis and management. Because trauma is a multisystem disease, multiple injuries may be present in the trauma patient.
- – Traumatic injuries of kidney and ureter
- – Bladder Injuries
- – Urethral Injuries
- – Testicular Injuries
- – Penile Injuries
- – Vaginal Injuries
- – Sexual assault
- – Child abuse
Traumatic injuries of kidney and ureter
KIDNEY INJURIES
Treatment for kidney injuries depends on the type and severity of the injury, and whether the patient has any other injuries.
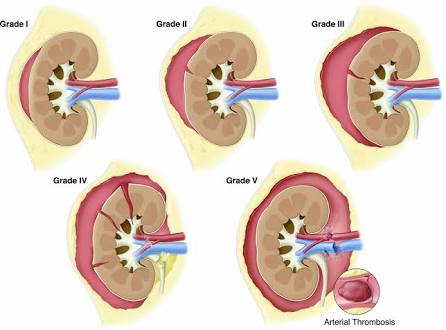
- – Blunt Injuries— In 85 percent of cases, injuries to the kidneys are minor, caused by a blunt trauma and do not require surgery. Treatment aims to stop any bleeding from the kidney. Hospital admission, bed rest and hydration are required until bleeding from the kidney stops and urine is clear.
- – Penetrating Injuries— Surgery is more likely for penetrating injuries, such as those from a gunshot wound, which can cause serious bleeding from the kidney. Patients also may have serious injuries to other parts of the abdomen, such as the bowel and liver.In these instances, surgical exploration and repair of the kidneys may be performed at the same time as surgery for other injured parts. Surgery aims to repair and preserve the injured kidneys. However, if the kidney is severely injured and beyond repair, surgical removal may be required.
URETERAL INJURIES
Injuries to the ureters — the tubes that connect each kidney to the bladder — are rare and usually occur during a difficult pelvic surgical procedure or from a gunshot wound. Treatment depends on the type and severity of injury.
- – Complete Disruption— Ureteral injuries that cause complete disruption, meaning that the ureter is torn into two pieces, require emergency surgical repair. The best outcome for surgical repair is prompt treatment at the time of injury.
- – Partial Injuries— Partial ureteral injuries, such as those that occur during a pelvic operation, often can be managed by a ureteral stent. Ureteral stents are thin tubes, called catheters, which are inserted into the ureter that carry urine, produced by the kidney down into the bladder.Ureteral stenting may be placed on a long-term basis, ranging from months to years, to bypass ureteral obstruction. Short-term stenting, ranging from weeks to months, may be placed during an open surgical procedure of the urinary tract to provide a mold around which healing can occur, or to divert the urinary flow away from areas of leakage.
BLADDER INJURIES
Bladder injuries are most often caused by an accident, such as a car accident, serious fall or a heavy object falling on the lower abdomen. Treatment depends on the type of injury.
- – Contusion Injury— In these types of injuries, the bladder wall is only bruised and does not rupture. Contusion injuries can be managed with a urethral catheter, which is a tube inserted into the bladder through the urethra, so that blood clots pass. Once the urine is clear and the patient stable, the catheter can be removed.
- – Extraperitoneal Rupture— These types of injuries can be managed with a urethral catheter, which is a tube inserted into the bladder through the urethra, to keep the bladder empty and allow the urine and blood to drain out into a collection bag. In most instances, a patient will heal within 10 days. However, large blood clots in the bladder or injuries involving the bladder neck require surgical repair.
- – Intraperitoneal Rupture— These ruptures require surgical repair to prevent urine from leaking into the abdomen. The repair is performed by making an incision in the abdomen and then sewing the tear closed. A catheter is left in the bladder for a few days to rest the bladder after surgery.
- – Penetrating Injuries— Penetrating injuries usually require surgical repair of any holes made in the bladder. In most instances, surrounding organs are injured and also require repair. A catheter is left in the bladder to drain the urine and blood as described above.
URETHEAL INJURIES
Management and treatment of urethral injuries can be complex and depends on the severity and location of injury, the patient’s health and whether any other injuries are present. In some cases, emergency surgical repair is recommended, but should be limited to select cases. As a general rule, initial suprapubic cystostomy, which involves placing a catheter in the bladder through the lower abdomen, is the safest and simplest option.
These are of two types:
- – Anterior
- – Located anterior to the membranous urethra
- – Straddle injuries, self-instrumentation
- – Posterior
- – Located in the membranous and prostatic urethra
- – Due to blunt trauma from massive deceleration
- – Often accompanies pelvic fracture
Evaluation of urethral trauma is done by:
- – Retrograde urethrogram
TESTICULAR INJURIES
Testicular injuries often occur due to a traumatic blow to the groin or scrotum, which can cause severe pain, nausea, vomiting and in some instances, lower abdominal tenderness. In these cases, a testicular ultrasound — a non-invasive test that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the testicles and other parts inside the scrotum — is usually performed to evaluate possible damage to the testicle. If a testicular fracture is diagnosed, surgical exploration and repair is required.
Clinical features of this trauma are:
- – Blunt trauma due to impingement against symphysis pubis
- – Will have contusion or rupture based on whether tunica albuginea is disrupted
- – Large, blue, tender scrotal mass (hematocele)
- – Testicular dislocation
- – Absent testicle
Evaluation
- – Scrotal ultrasound required for all blunt testicular injuries
PENILE INJURIES
Penile injuries can occur in various ways. For instance, penile fractures may occur during sexual intercourse and are usually surgically repaired. In other instances, placing obstructing rings around the base of the penis may lead to gangrene and urethral injuries. The obstructing objects can be removed without further damage. In addition, machinery accidents may cause damage to penile skin, which can be repaired by skin grafting.
Penile injuries often occur with urethral injuries. Therefore, when making a diagnosis of penile injuries, a urethrography — a test involving X-rays of the urethra — will be performed to identify any injuries or obstructions in this area.
Below are the various types of penile injuries:
- – Penile fracture
- – Penile contusion
- – Zipper injury to penis
- – Penile amputation
VAGINAL INJURIES
Vaginal injuries is defined as any injury to the female genital area – including the labia, vulva and/or vagina. Most cases of genital trauma occur accidentally and involve bruising, swelling and/or minor cuts that heal within a few days.
Primary pages
Contact us
Name : Dr. Amit Kumar Jha
Phone : 934 015 6457
Email : amitkumarjha2252@gmail.com
Address : OPD number 137, first floor, Bansal hospital, C sector Shahpura, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh. India. PIN – 462016
cheap replica watches uk
Buy perfect aaa Panerai replica watches uk wholesale shop.